Why Does the Neutral Point of a Large Generator Need to be Reliably Grounded?
Writer: admin Time:2025-09-19 13:58:59 Browse:588℃
Neutral Point Grounding of Generators: Focus on Stator Protection and System Stability
Generators are the core power sources of the grid. Their stator winding insulation is fragile, and faults can be extremely costly to repair. In addition, the generation system must avoid frequency and voltage oscillations caused by faults. Therefore, neutral point grounding design for generators emphasizes limiting fault current and protecting stator insulation.
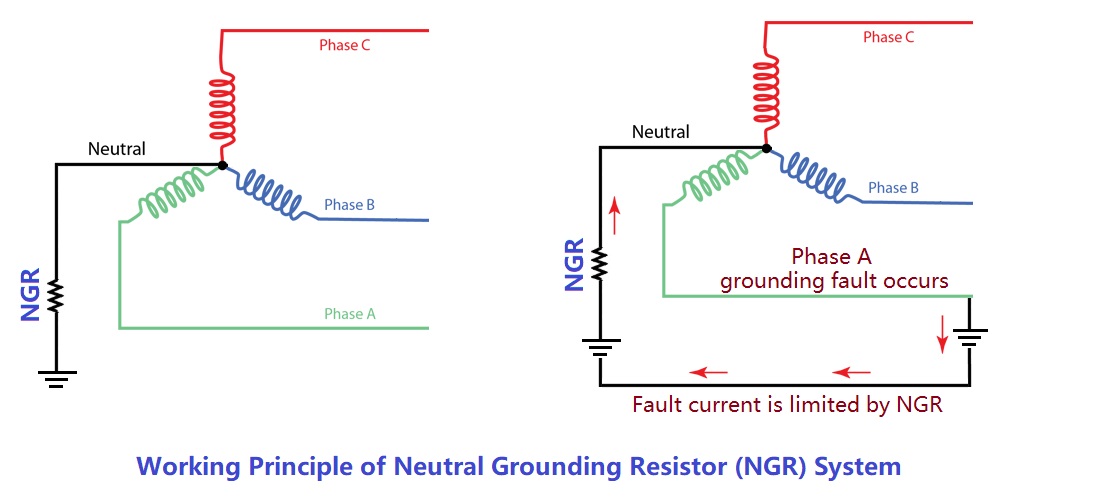
1. Large Steam / Hydro Turbine Generators: Neutral Point Grounded via High-Resistance
Application scenarios: Steam generators of 300 MW and above in thermal power plants; large hydro turbine generators (output voltages typically 10.5 kV or 15.75 kV).
Principle and purpose:
Ungrounded neutral: fault current is small but may cause intermittent arcs, damaging insulation.
Direct grounding: fault current can reach tens of kiloamperes, instantly burning the winding conductors.
If a single-phase-to-ground fault occurs in the stator winding:
Therefore, the generator neutral is usually grounded via a high-resistance resistor (several kilo-ohms), limiting the single-phase fault current to 5–10 A. This allows protection devices (e.g., stator ground protection) to operate reliably while preventing damage to the windings.
High-resistance grounding also suppresses overvoltage during faults, reducing the risk of system oscillations.
Example 1: In a 350 MW steam generator at a thermal power plant, the neutral is grounded via a 2000 Ω metal oxide resistor installed near the generator terminals. During operation, a single-phase fault occurred due to stator insulation aging. The fault current was limited to 8 A. The stator ground protection detected zero-sequence voltage, triggered an alarm, and coordinated generator load reduction. Operators safely shut down the generator within 10 minutes for repair, avoiding winding damage. Without high-resistance grounding, fault current could reach 5000 A, completely destroying the winding and requiring months of repair, with losses exceeding tens of millions RMB.
Example 2: A financial disaster recovery data center has two 2000 kW, 400 V diesel generators as backup power, with their neutrals grounded via 10 Ω high-resistance resistors. One day, a single-phase fault occurred due to insulation aging of a server rack power cable. The generator control system detected a 6.2 A fault current, triggered audible and visual alarms, and precisely displayed the fault location in the monitoring system. Because the fault current was effectively limited by the high-resistance grounding, no damage occurred to the generators or other distribution equipment. The generators continued supplying power, keeping critical systems (bank transaction backups, customer data storage) operational. Maintenance staff located and isolated the faulty cable within 8 minutes, avoiding production downtime or data loss.

2. Small Generators (e.g., Diesel Generators): Neutral Ungrounded or Grounded via Small Capacitor
Application scenarios: Factory backup diesel generators (<1000 kW, 400 V output), small hydro generators in remote areas.
Principle and purpose:
Small generators typically serve as emergency power, with small supply areas (single factory or village) and relatively balanced loads.
The probability of single-phase-to-ground faults is low.
Ungrounded neutral simplifies wiring and reduces cost; a small capacitor may be used to compensate capacitive current and prevent overvoltage.
Fault current is small (<1 A), allowing the generator to operate briefly under fault, maintaining emergency supply until the fault is cleared.
Example: A chemical plant has an 800 kW, 400 V backup diesel generator with an ungrounded neutral. During a plant-wide power outage, the generator supplied power. A single-phase fault occurred due to a pump cable insulation failure. The generator control system detected zero-sequence voltage and issued an alarm. The fault current was only 0.5 A, leaving generator operation unaffected. The cable was repaired within 30 minutes, with production equipment continuously powered, preventing production losses.
Related Articles:
How to Accurately Calculate the Neutral Grounding Resistance Value of a Transformer
Global Top 8 Neutral Grounding Resistor (NGR)Manufacturers
Transformer Neutral Grounding Methods and Applications for High-, Medium-, and Low-Voltage Systems
Solid, Resistance, and Ungrounded Systems — Which Is Safer for your Network?
Why Does the Neutral Point of a Large Generator Need to be Reliably Grounded?


CATEGORIES
- Neutral Grounding Resistor for Transformer
- Generator Neutral Grounding Resistor
- Low Voltage Neutral Grounding Resistor
- Neutral Grounding Arc Suppression Coils (Peterson Coil)
- Neutral Point Gap Grounding Protection Device
- Nitrogen Injection Fire Protection System for Transformer (NIFPS)
- Transformer Air-Cooled Control Equipment
- Nonlinear Neutral Grounding Equipment
LATEST NEWS
- Why Does the Neutral Point of a Large Generator Need to be Reliably Grounded?
- Transformer Neutral Grounding Methods and Applications for High-, Medium-, and Low-Voltage Systems
- How to Accurately Calculate the Neutral Grounding Resistance Value of a Transformer
- Global Top 8 Neutral Grounding Resistor (NGR)Manufacturers
- How to accurately calculate a 10 A neutral grounding resistor for a 13.8 kV system?
CONTACT US
WhatsApp: +86-18631228466
Tel: +86-312-5959618
Email: info@orionresistors.com
Add: No. 79, Fuchang Road, Zhongguancun Entrepreneurship Base, Baoding City,China